
Buckle up as we dive into the world of hyperthyroidism causes and symptoms! From autoimmune diseases to excess iodine intake, we’ll uncover the mysteries surrounding this condition in a fun and engaging way. Get ready to learn and be entertained!
Hyperthyroidism Causes
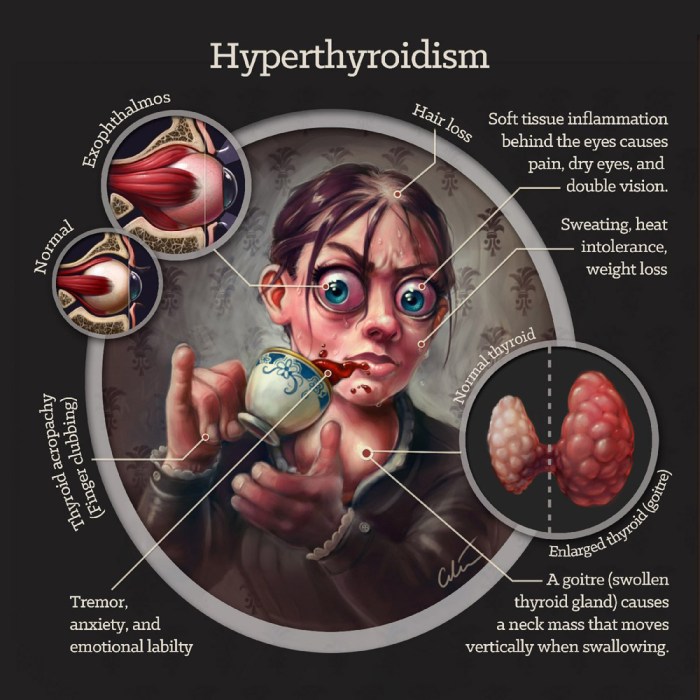
Hyperthyroidism is a condition characterized by the overproduction of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland. Several factors can contribute to the development of hyperthyroidism, including autoimmune diseases, hyperfunctioning thyroid nodules, and excess iodine intake.
Autoimmune Diseases and Hyperthyroidism
Autoimmune diseases, such as Graves’ disease, are a common cause of hyperthyroidism. In Graves’ disease, the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland, leading to the production of excessive thyroid hormones. This autoimmune disorder can result in symptoms such as weight loss, rapid heartbeat, and anxiety.
Hyperfunctioning Thyroid Nodules
Hyperfunctioning thyroid nodules, also known as toxic nodular goiter, are another cause of hyperthyroidism. These nodules are small lumps that develop in the thyroid gland and produce thyroid hormones independently of the body’s normal regulatory mechanisms. This overproduction of hormones can disrupt the balance in the body and lead to hyperthyroidism symptoms.
Excess Iodine Intake
Excess intake of iodine, either through diet or medication, can also trigger hyperthyroidism. Iodine is an essential nutrient required for the production of thyroid hormones. However, consuming too much iodine can cause the thyroid gland to become overactive and produce excessive amounts of hormones. This can result in hyperthyroidism symptoms like weight loss, tremors, and heat intolerance.
Hyperthyroidism Symptoms
Hyperthyroidism is a condition where the thyroid gland produces an excess of thyroid hormones, leading to various symptoms that can impact a person’s overall health and well-being.
Weight Loss, Rapid Heartbeat, and Tremors
- One of the common symptoms of hyperthyroidism is unexplained weight loss despite an increased appetite.
- Individuals may also experience a rapid or irregular heartbeat, known as palpitations, due to the overproduction of thyroid hormones.
- Tremors or shaking of the hands and fingers can also occur as a result of the increased metabolic rate associated with hyperthyroidism.
Impact on Metabolism and Energy Levels
- Hyperthyroidism speeds up the body’s metabolism, causing individuals to burn calories at a faster rate than normal.
- This increased metabolism can lead to feelings of fatigue and weakness, despite the excess energy being expended.
Psychological Symptoms: Anxiety and Irritability
- Anxiety, nervousness, and irritability are psychological symptoms commonly associated with hyperthyroidism.
- The overstimulation of the nervous system due to excess thyroid hormones can contribute to these emotional disturbances.
Less Common Symptoms: Heat Intolerance and Increased Sweating
- People with hyperthyroidism may experience intolerance to heat, feeling overly warm even in normal temperature environments.
- Increased sweating, particularly during physical activity or in warm conditions, can also be a less common symptom of hyperthyroidism.
Diseases STDs
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are infections that are spread through sexual contact. They can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites. Common STDs include chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, genital herpes, HIV/AIDS, and HPV.STDs like chlamydia and gonorrhea can have serious consequences if left untreated. It is important to be aware of the symptoms, prevention methods, and treatment options for these infections.
Chlamydia
Chlamydia is a common bacterial STD that can affect both men and women. Symptoms may include abnormal discharge, painful urination, and pelvic pain. If left untreated, it can lead to serious complications such as infertility.
- Prevention: Practicing safe sex, using condoms, and getting tested regularly can help prevent the spread of chlamydia.
- Treatment: Chlamydia can be treated with antibiotics. It is important to complete the full course of medication as prescribed by a healthcare provider.
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is another bacterial STD that can cause symptoms such as painful urination, abnormal discharge, and pelvic pain. If untreated, it can lead to infertility and other serious health problems.
- Prevention: Safe sex practices, regular screenings, and open communication with sexual partners can help prevent the spread of gonorrhea.
- Treatment: Gonorrhea is typically treated with antibiotics. It is essential to follow the prescribed treatment plan to ensure the infection is fully cleared.
Regular STD screenings are crucial for early detection and treatment of infections. Safe sexual practices, such as using condoms and limiting the number of sexual partners, can help reduce the risk of contracting STDs.Untreated STDs can have long-term consequences, including infertility, chronic pain, and an increased risk of HIV transmission. It is essential to prioritize sexual health and seek medical attention if you suspect you may have been exposed to an STD.
Health Acne
Acne is a common skin condition that occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil and dead skin cells. Hormonal imbalances, such as those seen in hyperthyroidism, can often play a role in the development of acne. When the body produces too much thyroid hormone, it can lead to an increase in sebum production, which can contribute to acne breakouts.
Causes of Acne
- Hormonal changes: Fluctuations in hormone levels, such as during puberty, menstrual cycles, or conditions like hyperthyroidism, can trigger acne.
- Excessive sebum production: Overproduction of oil by the skin glands can clog pores and lead to acne.
- Bacteria: Propionibacterium acnes, a type of bacteria that lives on the skin, can contribute to the development of acne.
- Inflammation: Inflammatory responses in the skin can worsen acne symptoms.
Managing and Preventing Acne Breakouts
- Cleanse your skin regularly: Washing your face with a gentle cleanser can help remove excess oil and prevent acne.
- Avoid touching your face: Touching your face can transfer bacteria and dirt, exacerbating acne breakouts.
- Use non-comedogenic products: Choose skincare and makeup products that are labeled non-comedogenic to prevent clogged pores.
- Maintain a healthy diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help support skin health and reduce acne.
Role of Diet, Skincare, and Lifestyle Factors
- Diet: Some studies suggest that dairy, high-glycemic foods, and certain fats may worsen acne.
- Skincare: Using products with ingredients like salicylic acid or benzoyl peroxide can help treat acne.
- Lifestyle: Factors like stress, lack of sleep, and smoking can contribute to acne development.
Types of Acne and Treatment Options
- Whiteheads and blackheads: Mild forms of acne that can often be treated with over-the-counter products containing ingredients like benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid.
- Papules and pustules: Inflammatory acne lesions that may require prescription medications like topical or oral antibiotics.
- Cysts and nodules: Severe forms of acne that can cause scarring and may require more aggressive treatments like isotretinoin.
Hand Wrist Pain
Hand and wrist pain can be debilitating and affect daily activities. It is important to understand the common causes of hand and wrist pain, including conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome and arthritis. Ergonomic tips can help prevent hand and wrist pain, and knowing when to seek medical attention for persistent pain is crucial.
Common Causes of Hand and Wrist Pain
Hand and wrist pain can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Repetitive motion injuries
- Fractures or sprains
- Nerve compression
- Arthritis
- Tendonitis
Conditions Leading to Wrist Pain
Conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome and arthritis can lead to wrist pain. Carpal tunnel syndrome occurs when the median nerve, which runs from the forearm into the palm of the hand, becomes compressed at the wrist. Arthritis can cause inflammation and stiffness in the joints, leading to pain and limited mobility.
Ergonomic Tips for Preventing Hand and Wrist Pain
Proper ergonomics can help prevent hand and wrist pain. Some tips include:
- Ensure proper wrist positioning when typing or using a computer mouse
- Take breaks to stretch and rest your hands and wrists
- Use tools and equipment that are designed to reduce strain on the hands and wrists
- Maintain good posture to prevent unnecessary stress on the hands and wrists
When to Seek Medical Attention
If hand and wrist pain persists or worsens despite home remedies and ergonomic adjustments, it is important to seek medical attention. A healthcare professional can provide a proper diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment options to relieve pain and restore function.
Health Arthritis

Arthritis is a condition that causes inflammation in the joints, leading to pain, stiffness, and decreased range of motion. There are different types of arthritis, with the most common ones being osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoarthritis is typically caused by wear and tear on the joints over time, while rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the joints.
Types of Arthritis
- Osteoarthritis: Caused by wear and tear on the joints, leading to pain and stiffness.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: An autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks the joints, causing inflammation and pain.
Symptoms and Risk Factors
- Symptoms of arthritis include joint pain, swelling, stiffness, and reduced range of motion.
- Common risk factors for arthritis include age, family history, obesity, and previous joint injuries.
Treatment Options
- Treatment for arthritis focuses on relieving pain, reducing inflammation, and improving joint function.
- Options include medications, physical therapy, lifestyle changes, and in severe cases, surgery.
Importance of Exercise and Healthy Weight
Regular exercise can help improve joint flexibility, strengthen muscles, and reduce pain associated with arthritis. Maintaining a healthy weight is also crucial, as excess weight puts added stress on the joints, worsening arthritis symptoms.
Impact on Daily Activities
Arthritis can significantly impact daily activities such as walking, climbing stairs, and even simple tasks like opening jars or turning doorknobs. The pain and stiffness caused by arthritis can affect quality of life and overall well-being.
Quit Smoking
Smoking poses serious health risks and can lead to various diseases, including lung cancer, heart disease, and respiratory issues. It also increases the risk of developing hyperthyroidism and other thyroid disorders.
Strategies for Quitting Smoking
- Set a quit date and stick to it.
- Seek support from friends, family, or a support group.
- Consider nicotine replacement therapy or medications prescribed by a healthcare provider.
- Engage in activities to distract yourself from cravings, such as exercise or hobbies.
- Avoid triggers that make you want to smoke, like alcohol or stressful situations.
Benefits of Quitting Smoking
- Improved lung function and decreased risk of respiratory infections.
- Reduced risk of heart disease, stroke, and cancer.
- Improved sense of taste and smell.
- Increased energy levels and overall well-being.
Resources and Support for Quitting Smoking
There are various resources available to help individuals quit smoking, including:
- National Quitline: A free telephone counseling service to provide support and guidance.
- Online support groups and forums for individuals to connect with others going through the same journey.
- Behavioral therapy programs to address the psychological aspects of nicotine addiction.
- Mobile apps and text messaging programs for motivation and tracking progress.
Health Nutrition
Proper nutrition is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being. A balanced diet provides the necessary nutrients to support bodily functions, energy levels, and disease prevention.
Key Nutrients and Their Roles
- Vitamins: Essential for various metabolic processes, immune function, and overall health. For example, Vitamin C is important for collagen production and immune system support.
- Minerals: Play a crucial role in bone health, nerve function, and fluid balance. Examples include calcium for bone strength and iron for oxygen transport.
- Macronutrients: Carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are needed in larger quantities to provide energy, support growth, and maintain bodily functions.
Meal Planning and Healthy Eating Habits
- Plan balanced meals with a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Avoid processed foods high in sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats.
- Stay hydrated by drinking an adequate amount of water throughout the day.
- Practice mindful eating by paying attention to hunger cues and eating slowly.
Nutrition and Health Impact
- Weight Management: Consuming nutrient-dense foods and controlling portion sizes can help with weight maintenance or weight loss goals.
- Disease Prevention: A diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants can reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and cancer.
Health Thyroid
The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped organ located in the neck that plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism, growth, and energy levels in the body. It produces hormones that control various functions in the body, such as heart rate, body temperature, and digestion.
Thyroid Disorders
- Hypothyroidism: This condition occurs when the thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones, leading to symptoms like fatigue, weight gain, and depression.
- Hyperthyroidism: In contrast, hyperthyroidism is a condition where the thyroid gland produces an excess of hormones, causing symptoms such as weight loss, rapid heartbeat, and anxiety.
Symptoms and Causes
- Thyroid conditions can present a variety of symptoms including fatigue, weight changes, mood swings, and changes in heart rate.
- Common causes of thyroid disorders include autoimmune conditions, iodine deficiency, and genetic factors.
Diagnosis and Treatment
- Diagnosis of thyroid disorders involves blood tests to measure hormone levels, imaging tests like ultrasound, and sometimes a biopsy of the thyroid gland.
- Treatment options for thyroid conditions may include medication to regulate hormone levels, radioactive iodine therapy, or in severe cases, surgery to remove part or all of the thyroid gland.
Importance of Thyroid Health
The thyroid gland is essential for maintaining overall well-being, as it regulates many bodily functions. Ensuring proper thyroid health through regular check-ups, a balanced diet, and appropriate treatment can help prevent complications and maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Developmental Disabilities
Developmental disabilities refer to a group of conditions due to impairment in physical, learning, language, or behavior areas. Common types include autism spectrum disorder and Down syndrome. These disabilities typically manifest during infancy or childhood and can impact an individual’s daily functioning and independence.
Types of Developmental Disabilities
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): Characterized by challenges in social skills, communication, and repetitive behaviors.
- Down Syndrome: Caused by an extra chromosome 21, leading to intellectual disabilities and distinct facial features.
- Cerebral Palsy: Affects movement and muscle coordination due to brain damage before, during, or shortly after birth.
Early Signs, Diagnosis, and Intervention
Early detection is crucial for effective intervention in developmental disabilities. Signs may include delays in reaching milestones, difficulty with learning or communication, and unusual behaviors. Diagnosis involves comprehensive evaluations by healthcare professionals and specialists.
Early intervention services such as speech therapy, occupational therapy, and special education programs can help individuals with developmental disabilities reach their full potential.
Challenges Faced by Individuals and Families
- Social Stigma: Individuals with developmental disabilities may face discrimination and lack of social acceptance.
- Financial Strain: Medical expenses, therapy costs, and specialized care can be financially burdensome for families.
- Caregiver Stress: Family members often experience emotional and physical strain when caring for loved ones with developmental disabilities.
Resources and Support Services
There are various resources and support services available for individuals with developmental disabilities and their families to enhance quality of life and promote inclusion.
These may include community programs, support groups, respite care services, and advocacy organizations.
Health Autism
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition that affects social interaction, communication, and behavior. It is characterized by a wide range of symptoms and levels of impairment, leading to the term “spectrum.”Early signs of autism may include delays in speech and language development, repetitive behaviors, difficulties in social interactions, and sensory sensitivities. Diagnosis typically involves a comprehensive evaluation by healthcare professionals, including developmental pediatricians, psychologists, and speech therapists.Treatment options for autism often involve a multidisciplinary approach, including behavioral therapies, speech therapy, occupational therapy, and sometimes medication to manage specific symptoms.
Early intervention is crucial in improving outcomes for individuals with autism.
Therapies and Interventions
- Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA): A structured therapy that focuses on improving specific behaviors and skills.
- Speech Therapy: Helps individuals with autism improve their communication skills and language development.
- Occupational Therapy: Aims to enhance daily living skills, fine motor skills, and sensory processing.
- Social Skills Training: Teaches individuals with autism how to navigate social interactions and relationships.
- Sensory Integration Therapy: Addresses sensory sensitivities and helps individuals regulate their responses to sensory input.
Health Supplements
Supplements play a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being by providing essential nutrients that may be lacking in our diet. However, it is important to consult with healthcare providers before taking any supplements to ensure they are safe and appropriate for your individual needs.
Types of Supplements
- Vitamins: These are organic compounds that our body needs in small amounts to function properly. They can help support immune function, energy production, and overall health.
- Minerals: These are inorganic elements that are essential for various bodily functions, such as bone health, nerve function, and muscle contraction.
- Herbal Supplements: These are products made from plants or plant extracts that are used for their medicinal properties. They can help with a variety of health issues, such as stress, sleep, and digestion.
Role of Supplements
Supplements can complement a healthy diet and lifestyle by filling in nutrient gaps and supporting specific health goals. They can provide additional support for overall well-being, energy levels, immune function, and more. It is important to choose high-quality supplements from reputable brands to ensure safety and efficacy.
Ending Remarks
In conclusion, hyperthyroidism is a complex condition with a range of causes and symptoms. By understanding these factors, we can better navigate the world of thyroid health and take proactive steps towards managing this condition effectively. Stay informed, stay healthy!
Questions and Answers
What role does excess iodine intake play in causing hyperthyroidism?
Excess iodine can lead to an overactive thyroid by triggering the gland to produce too much hormone, resulting in hyperthyroidism.
Can hyperthyroidism cause psychological symptoms like anxiety?
Absolutely! Hyperthyroidism can manifest as anxiety, irritability, and other psychological symptoms due to the impact on hormone levels in the body.
Are there less common symptoms of hyperthyroidism apart from weight loss and rapid heartbeat?
Yes, symptoms like heat intolerance and increased sweating can also be signs of hyperthyroidism, indicating an overactive thyroid.
How does hyperthyroidism affect energy levels and metabolism?
Hyperthyroidism can rev up metabolism, leading to weight loss and increased energy levels due to the overproduction of thyroid hormones.





